最近做的项目需要详细了解geojson,因此查了一些资料,现在整理一份标准格式的记录,要理解本文需要首先了解json的基本知识,这里不过多展开,可以去参考w3school上的教程,简言之,json是通过键值对表示数据对象的一种格式,可以很好地表达数据,其全称为JavaScript Object Notation(JavaScript Object Notation),正如这个名称,JavaScript和json联系紧密,但是json可以应用的范围很广,不止于前端,它比XML数据更轻量、更容易解析(某种角度上说xml可以更自由地封装更多的数据)。很多编程语言都有对应的json解析库,例如Python的json库,C#的Newtonsoft.Json,Java的org.json。geojson是用json的语法表达和存储地理数据,可以说是json的子集。
例如下面就是一个点数据:
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
| {
"type": "FeatureCollection",
"features": [
{"type":"Feature",
"properties":{},
"geometry":{
"type":"Point",
"coordinates":[105.380859375,31.57853542647338]
}
}
]
}
|
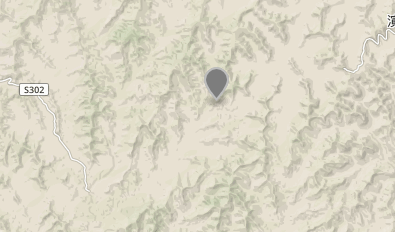
(注:以下geojson的效果截图都来自geojson.io在线生成)
geojson将所有的地理要素分为Point、MultiPoint、LineString、MultiLineString、Polygon、MultiPolygon、GeometryCollection。首先是将这些要素封装到单个的geometry里,然后作为一个个的Feature(也就是要素);要素放到一个要素集合里,从树状结构来理解FeatureCollection就是根节点,表示为:
1
2
3
4
| {
"type": "FeatureCollection",
"features": []
}
|
所有地理要素放在features的列表里。
点要素Point
点要素是最简单的,类型type对应Point,然后坐标是一个1维的数组,里面有两个元素(如果是立体的坐标就是三维x,y,z),分别为经度和纬度。properties里面可以封装各种属性,例如名称、标识颜色等等。
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
| {"type":"Feature",
"properties":{},
"geometry":{
"type":"Point",
"coordinates":[105.380859375,31.57853542647338]
}
}
|
多点要素MultiPoint
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
| {"type":"Feature",
"properties":{},
"geometry":{
"type":"MultiPoint",
"coordinates":[[105.380859375,31.57853542647338],
[105.580859375,31.52853542647338]
]
}
}
|
其核心坐标:
1
2
| 105.380859375,31.57853542647338
105.580859375,31.52853542647338
|
线要素LineString
线要素就是指线段,记录的是线的端点坐标,可视化时会按照记录顺序联结。对于曲线(如贝塞尔曲线)目前还没有很好的表达,但是在地理数据中,曲线一般会用LineString去拟合,现实地理世界中也没有标准的曲线地理要素。
线要素的坐标coordinates里的二维数组和多点要素基本一样,区别就在type上了。
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
| {"type":"Feature",
"properties":{},
"geometry":{
"type":"LineString",
"coordinates":[[105.6005859375,30.65681556429287],
[107.95166015624999,31.98944183792288],
[109.3798828125,30.031055426540206],
[107.7978515625,29.935895213372444]]
}
}
|
对应的Kml表达:
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
| <Placemark>
<ExtendedData></ExtendedData>
<LineString>
<coordinates>108.65753173828125,34.1873818599505 108.72413635253905,34.25154099726973 108.77151489257812,34.16977214177208 108.88481140136719,34.229970811273084
</coordinates>
</LineString>
</Placemark>
|
MultiLineString
也是一个三维数组(和多边形一样);
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
| {"type":"Feature",
"properties":{},
"geometry":{
"type":"MultiLineString",
"coordinates":
[
[
[105.6005859375,30.65681556429287],
[107.95166015624999,31.98944183792288],
[109.3798828125,30.031055426540206],
[107.7978515625,29.935895213372444]
],
[
[109.3798828125,30.031055426540206],
[107.1978515625,31.235895213372444]
]
]
}
}
|
多边形Polygon
注:单个多边形是一个3维数组,可以包含多个二维数组,这种情况和MultiPolygon效果很像。
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
| {"type":"Feature",
"properties":{},
"geometry":{
"type":"Polygon",
"coordinates":[
[
[106.10595703125,33.33970700424026],
[106.32568359375,32.41706632846282],
[108.03955078125,32.2313896627376],
[108.25927734375,33.15594830078649],
[106.10595703125,33.33970700424026]
]
]
}
}
|
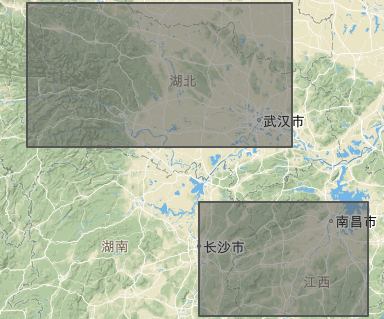
多多边形MultiPolygon
type 1 两个不会相交的多边形
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
| {
"type": "Feature",
"properties": {},
"geometry": {
"type": "MultiPolygon",
"coordinates":
[
[
[
[109.2041015625,30.088107753367257],
[115.02685546875,30.088107753367257],
[115.02685546875,32.7872745269555],
[109.2041015625,32.7872745269555],
[109.2041015625,30.088107753367257]
]
],
[
[
[112.9833984375,26.82407078047018],
[116.69677734375,26.82407078047018],
[116.69677734375,29.036960648558267],
[112.9833984375,29.036960648558267],
[112.9833984375,26.82407078047018]
]
]
]
}
}
|
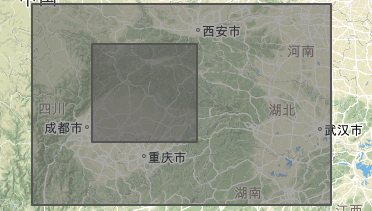
type 2 两个镶套的多边形
小的在前面,范围大的在后面,用上4个中括号,但效果不是有洞的
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
| {
"type": "Feature",
"properties": {},
"geometry": {
"type": "MultiPolygon",
"coordinates":
[
[
[
[101.6455078125,27.68352808378776],
[114.78515624999999,27.68352808378776],
[114.78515624999999,35.209721645221386],
[101.6455078125,35.209721645221386],
[101.6455078125,27.68352808378776]
]
],
[
[
[104.2822265625,30.107117887092357],
[108.896484375,30.107117887092357],
[108.896484375,33.76088200086917],
[104.2822265625,33.76088200086917],
[104.2822265625,30.107117887092357]
]
]
]
}
}
|
type 3 有孔洞的多边形
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
| {
"type": "Feature",
"properties": {},
"geometry": {
"type": "MultiPolygon",
"coordinates":
[
[
[
[101.6455078125,27.68352808378776],
[114.78515624999999,27.68352808378776],
[114.78515624999999,35.209721645221386],
[101.6455078125,35.209721645221386],
[101.6455078125,27.68352808378776]
],
[
[104.2822265625,30.107117887092357],
[108.896484375,30.107117887092357],
[108.896484375,33.76088200086917],
[104.2822265625,33.76088200086917],
[104.2822265625,30.107117887092357]
]
]
]
}
}
|
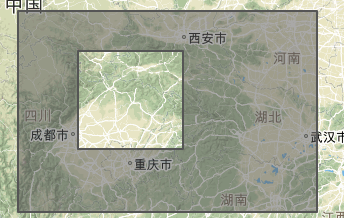
可以仔细去品味type2和type3的区别。它们对应的kml表达区别是比较大的。
GeometryCollection
GeometryCollection是多种基本地理要素的集合,就是里面可以包含点、线、面要素。
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
| {
"type": "GeometryCollection",
"geometries": [
{
"type": "Point",
"coordinates": [108.62, 31.02819]
}, {
"type": "LineString",
"coordinates": [[108.896484375,30.1071178870],
[108.2184375,30.91717870],
[109.5184375,31.2175780]]
}]
}
|
GeometryCollection不需要放在FeatureCollection里:
1
2
3
4
| {
"type": "FeatureCollection",
"features": []
}
|
geojson里面还有其他标签表达其他的属性,如外包矩形等,其中特别重要的是坐标系统,一般里面的坐标默认为WGS84,当然也可以是其他坐标系统的坐标,但是要标识。这部分内容之后再补充了。
更具体的内容可以参考rfc7946。



